Understanding the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
Susan Kelly
Jan 22, 2024
This legal entity is known as a "Special Purpose Vehicle" (SPV). The SPV is a separate legal entity with its assets and obligations. Typically, they are designed to achieve a certain goal, such as minimizing financial risk. If the parent firm falls bankrupt, the SPV can continue to operate independently.
"Bankruptcy remote" is a term that refers to a company's operations being limited to acquiring and funding certain assets or projects. Partnerships, limited partnerships, and joint ventures are among the most common types of special purpose vehicles. Furthermore, in some situations, the SPV must not be owned by the firm for which it was founded.
Understanding the SPV
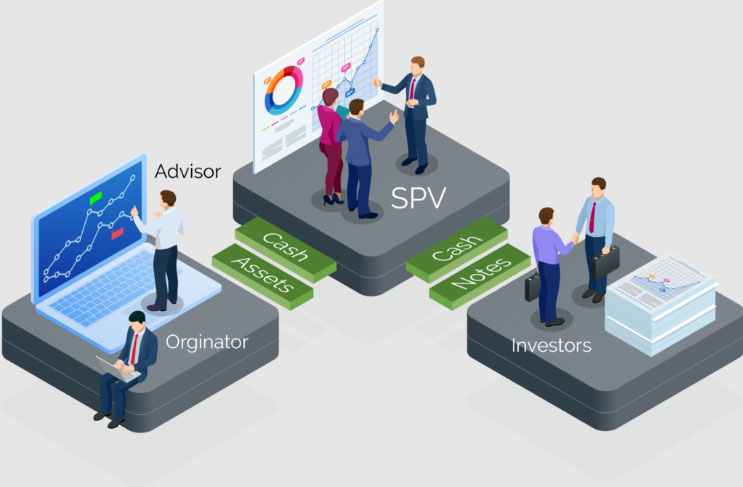
A parent corporation uses a to securitize assets in a separate entity that is frequently off the balance sheet. You can use it to take on a hazardous project while shielding the parent firm from the most severe consequences of its failure. SPVs can also be founded specifically to secure financing for investors so that they can be confident in their returns.
SPV operations are restricted to the acquisition and financing of specified assets, and this distinct business structure is used to protect investors from the risks associated with those activities. An SPV can facilitate swaps derivative products.
Among other alternatives, a firm can create an SPV as a partnership, trust, corporation, or limited liability company. It may be set up to be owned, managed, and funded by a third party. In any event, SPVs assist businesses in various ways, including asset securitization, joint venture formation, asset isolation, and a variety of other financial operations.
SPV: How Enron Used It?
Several examples of SPVs being misused, like the enormous financial collapse of Enron Corp. in Houston in 2001. When the company's stock was soaring, Enron transferred substantial amounts of shares to a special purpose entity in exchange for cash or a note.
It then utilized the stock to hedge assets held on its balance sheet through the special purpose entity. Enron insured the value of the special purpose vehicle to decrease risk. To put it another way, the values of the special purpose vehicles fell with Enron's stock price, and the guarantees had to be used.
Enron's abuse of SPVs was only one of several accounting gimmicks the company employed, but it was a major factor in its sudden demise. The financial downfall of Enron was a direct result of the company's inability to pay its creditors and investors.
Before its conclusion, it provided a balance sheet for both the corporation and its special purpose entities. Everyone could see that it had a conflict of interest. However, few investors could see the full scope of the problem.
What are the Uses of SPV
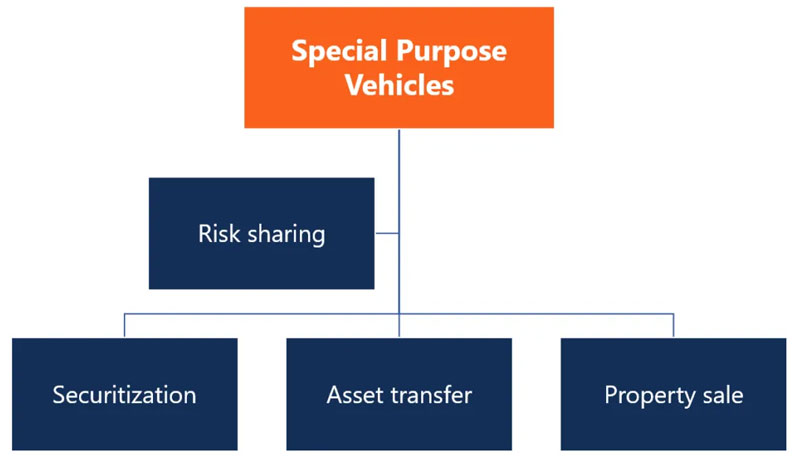
SPVs are typically created for the following reasons:
Sharing of Risks
A project undertaken by a company can carry a large amount of risk. It is possible to legally separate and distribute the risks of a project by establishing an SPV.
Securitization
Creating an SPV for securitizing loans is rather frequent. By forming an SPV, a bank may segregate the loans from its other responsibilities when releasing home loan securities from a pool of loans. This permits investors in mortgage-backed securities to obtain repayment for these loans ahead of other creditors.
Transfer of an Asset
The transferability of some assets is more difficult than others. A company can own these assets by forming a special purpose vehicle (SPV). They can easily sell the SPV as part of an M&A procedure when they want to transfer the assets.
Sale of Property
A firm may set up a special purpose vehicle (SPV) to hold the assets it intends to sell to avoid paying capital gains taxes. There is no need to pay property sales tax if it sells its SPV instead of real estate holdings.
What are the SPVs used for?
A special purpose vehicle is a subsidiary corporation founded for a specific purpose or activity. Structured finance applications such as asset securitization and joint ventures, property agreements, or the isolation of parent company assets and risks are prominent uses of SPVs. SPVs have been used in several financial and accounting scandals, although they have numerous legal purposes.
SPV: What Does it Mean for Investors?
Individual investors need to keep an eye out for corporations that set up SPVs since that might influence their choice to buy stock in that company. Participants in an SPV's funding should understand the SPV's objective, financial position, and predicted asset performance. Investors should be aware of this if the parent business does not display the SPV as an asset on its balance sheet.
An SPV's lack of a proven track record and reputation makes it riskier to invest directly in an SPV than in a more established company. Many investors lack a comprehensive understanding of their investments.